1. Why Must Laparoscopic Trocars Undergo Leak Testing?
Laparoscopic trocars are critical channels for delivering endoscopes or surgical instruments into body cavities during minimally invasive surgeries. They must exhibit excellent sealing performance to ensure smooth surgical procedures:
| Issue | Consequence |
|---|---|
| 🔸 Seal Failure | CO₂ gas leakage, leading to decreased pneumoperitoneum pressure and restricted surgical visibility; |
| 🔸 Trocar Channel Leakage | Increased risk of infection and postoperative complications; |
| 🔸 Poor Hermeticity | Failure to comply with medical device regulations (e.g., EN ISO 80369, YY/T 0466); |
| 🔸 Disposable Trocars Without Pre-Shipment Seal Testing | Difficulty in tracing batch-wide risks. |
Therefore, using high-precision leak testers to evaluate key areas such as the trocar body, seal valve ports, and catheter interfaces is essential for ensuring medical safety and regulatory compliance.
In 2022, a Zhejiang-based medical device company applied for EU CE certification for its disposable laparoscopic trocars. During third-party laboratory testing, the trocar valve seals were found insufficient, with CO₂ simulation tests exceeding leakage limits, resulting in certification rejection. Subsequently, the company introduced micro-leak-level leak testers (mass flow method), setting a leakage standard of ≤0.05 sccm and implementing 100% full inspection for each trocar. This successfully passed certification and elevated the product's market positioning, enabling entry into German and Italian markets.
2. Common Hermeticity/Seal Testing Methods
| Testing Method | Description |
|---|---|
| 🔹1. Mass Flow Method | Real-time monitoring of CO₂ channels or seal interfaces for
micro-leaks; High detection rate, suitable for medical micro-leak requirements (sccm level); Non-destructive, ideal for disposable or reusable trocar testing. |
| 🔹2. Pressure Decay Method (Differential Pressure) | Detects pressure drop in cavities after pressurization; High efficiency, suitable for structurally simple or high-volume trocar testing. |
| 🔹3. Water Immersion Method (For R&D/Failure Analysis) | Inflates the trocar and submerges it in water to observe
bubbles; Used only for R&D or sampling, not suitable for mass production. |
3. Recommended Testing Areas and Process (Using Mass Flow Method as an Example)
| Testing Area | Description |
|---|---|
| ✅ Trocar Valve Sealing Cavity | Can be tested individually or jointly |
| ✅ Cannula Channel (Simulating CO₂ Pathway) | Can be tested individually or jointly |
| ✅ Connector/Interface Sealing Structure | Can be tested individually or jointly |
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Fixture Sealing | Mount the trocar in a custom hermetic testing fixture to seal the test area; |
| Pressurization | Inject clean, dry gas (e.g., nitrogen, air) to the set test pressure (20~50 kPa); |
| Stabilization & Testing | Maintain constant pressure for a set duration while monitoring leakage flow; |
| Judgment Criteria | The leak tester automatically determines if leakage exceeds the set threshold; |
| Sorting & Output | NG products are automatically rejected or diverted, with test data recorded and archived. |
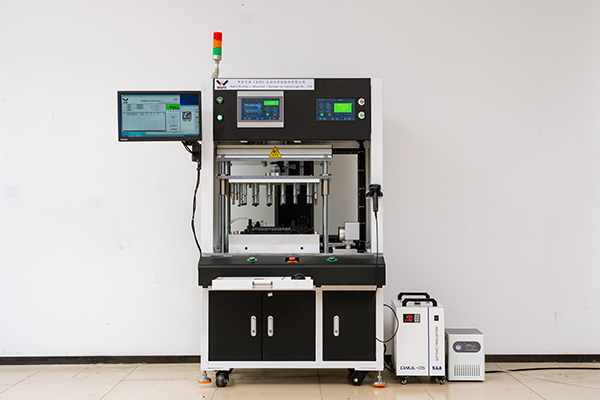
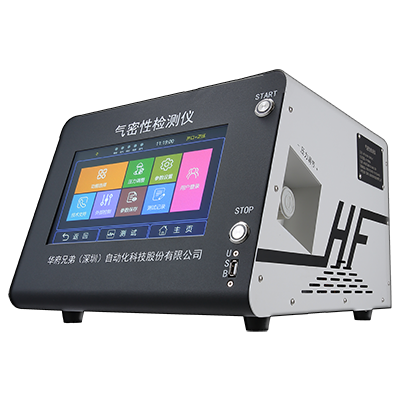
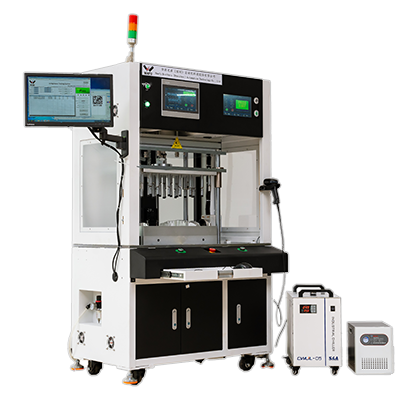
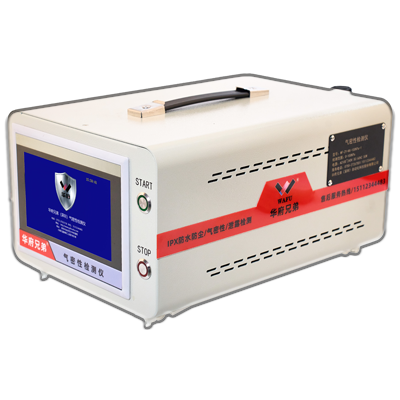
Recommended Products






