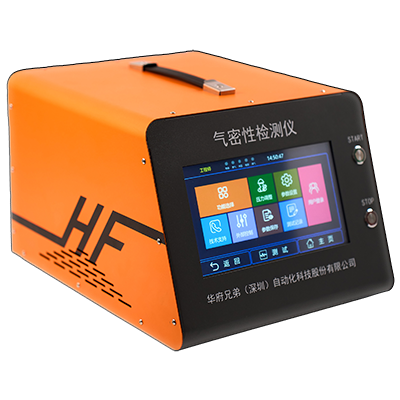
1. Cylindrical Lithium-ion Batteries
Cylindrical lithium-ion batteries are widely used in power tools, electric bicycles, energy storage systems, and electric vehicles. They contain flammable electrolytes and are typically encased in metal shells. Poor sealing may lead to the following issues:
| Issue | Detailed Description |
|---|---|
| Safety Risks | Air or moisture infiltration may trigger internal chemical reactions, causing swelling, leakage, short circuits, or even fire and explosion. |
| Performance Degradation | Minor leaks can reduce battery capacity, increase internal resistance, and affect lifespan and charge/discharge performance. |
| Quality Instability | Poor sealing leads to lower yield rates, higher repair rates, and impacts production consistency. |

A power tool manufacturer received customer feedback about severe battery swelling after mass shipment. Investigation revealed micro-leaks caused by improperly compressed sealing rings in some cylindrical cells. After implementing leak testers for 100% inspection, the defect rate dropped from 1.5% to 0.2% within two weeks, significantly improving customer satisfaction.
2. For cylindrical batteries, leak testing primarily focuses on the top seal, terminal posts, and safety valves. Suitable leak detection methods include:
| Method No. | Method Name | Application Scenario | Detailed Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Differential Pressure/Pressure Decay Method | Medium precision requirements | The battery is placed in a test chamber, pressurized with gas, and internal pressure changes are monitored to determine sealing integrity. |
| 2 | Mass Flow Method | High precision requirements | Uses flow meters to precisely measure leakage rates, suitable for energy storage or power battery cells. |
| 3 | Helium Leak Detection | Extremely high sealing requirements | Uses helium as tracer gas with mass spectrometry for micro-leak detection, typically for military or special medical batteries. |
3. Testing Procedure (Using Pressure Decay Method as Example)
| Step No. | Specific Procedure |
|---|---|
| 1 | Prepare battery samples: Select cylindrical lithium batteries for testing, ensuring no visible deformation or contamination. |
| 2 | Place in test chamber: Position battery correctly in sealed test chamber. |
| 3 | Inject test gas: Pressurize chamber to set value (e.g., 200kPa). |
| 4 | Stabilization: Allow stabilization time (e.g., 3 seconds) for environmental balance. |
| 5 | Measure leakage: Record pressure drop changes in chamber. |
| 6 | Result determination: Compare against leakage standard (e.g., ≤0.5Pa/s) for pass/fail judgment. |
| 7 | Output results: System automatically determines OK/NG, records data and uploads to MES system. |
Leak testing for cylindrical lithium-ion batteries is crucial for ensuring safety, performance stability, and quality control.
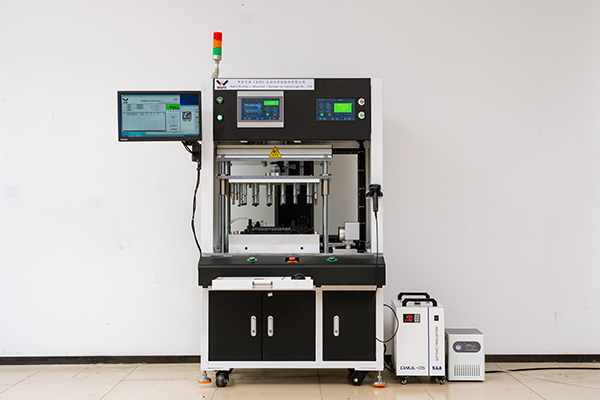
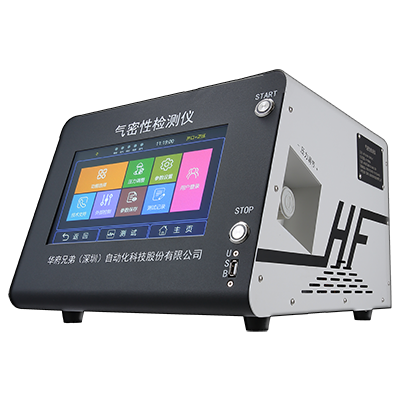
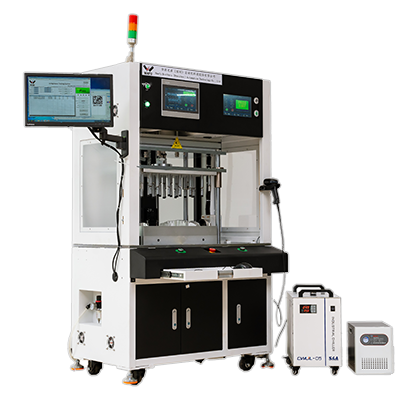
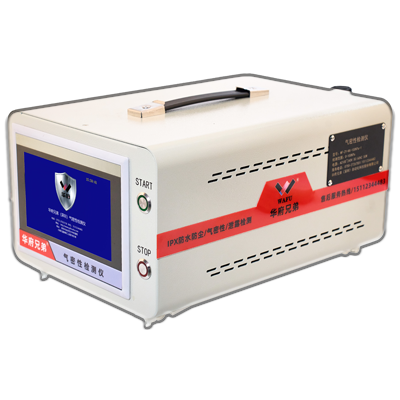
Recommended Products